Sometimes, you can observe slowness on your website. It means you are about to face a problem with the website. Maybe an indicator too! People would conclude by assuming a reason as overload in server and take a step to reduce the load in server. The technical person will ask you for some reports called traceroute and ping. To read the traceroute report, it is not necessary to be only a technical support executive. You can even take pride to read it!
Without any dependency, we need to analyze the problem right! So, that we can manage and sort out the issue quickly. In this article, we are going to explain how a traceroute can be read even if you are not a technical person. Next time, if your website gives a slow response then you can take a traceroute report and check the status for further confirmation.
What is traceroute mean?
The connection between the website and computer gives a path of points that connects one to one. You can even assume it as a dot-connecting like a chain so that your computer gets the access point of the website immediately. If you are at home or office, the router gives a signal first then goes along with the ISP for connecting the main frequency. There you can see more and more junctions but it won’t go out from the Internet highway and reaches the web server safely.
Here comes the role of traceroute! The path follows from the signal which goes in and around the internet to get connected to the website is known as traceroute. With the guidance of route, the traceroute gives the response time without fail by analyzing the junctions or stops at regular intervals. If you find the time was taken too much in traceroute so, you can confirm there is a problem in your website. In technical terms, they would say as hops instead of stops.
Let us explain how to follow the map of traceroute:
Here, you can see the traceroute report:
As per your request traceroute will start its process and report to you immediately.
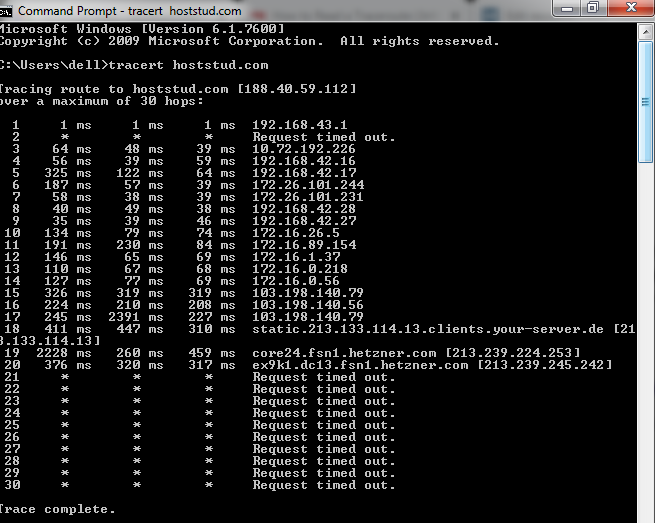
In the above report, you can see more rows and columns. As said previously, the route will be traveled with you even if it has a long go. So, the hop is represented as rows, and see the signal step in which direction it moves from one to one. It is known as a check-in point. The rows are categorized into five columns.
This is a sample row with five columns:
10
81 ms 74 ms 74 ms
205.134.225.38
You can consider like
hop is 10 – You can have a count like 10 hops are used here.
RTT1 is 81ms
RTT2 is 74ms
RTT3 is 74ms
IP address: 205.134.225.38
RTT is represented as round trip time. It takes a trip from packet to one essential point and later it reaches the computer. You are well known that ms is nothing but milliseconds. Signal packets are divided into three modes as per traceroute order.
Hop time checks:
Whenever you want to analyze the traceroute, check the round trip time for more pieces of information. Sometimes, you won’t know the existence of the problem due to the increase in time of latency. Give an overall glance at the report and understand the basic requirement first! Up to the United States, if they met trip for 150ms then it’s a long journey but for us, it’s a casual thing. We shouldn’t leave it casually because later it may end up with big issues than we expect.
When latency time increases more than expectation: If the level of the latency reaches more than the target point then please confirm that the issue has been started up in hop. Keep your eye on packets so that, you won’t lose them even if the hop increases at a certain point.
1
10 ms 7 ms 9 ms
172.16.10.2
2
78 ms 100 ms 32 ms
ip10-167-150-2.at.at.cox.net [70.167.150.2]
3
78 ms 84 ms 75 ms
100ge7-1.core1.nyc4.he.net [184.105.223.166]
4
782 ms 799 ms * ms
10gr10-3.core1.lax1.he.net [72.52.92.226]
5
* ms 899 ms 901 ms
10g1-3.core1.lax2.he.net [72.52.92.122]
6
987 ms 954 ms 976 ms
205.134.225.38
7
1002 ms 1011 ms 999 ms
www.hoststud.com [192.145.237.216]
What would happen if latency increases only in the middle point?
Just imagine a situation – Your latency point is normal at starting and ending. But, suddenly it increases in the middle what would be your next step? Don’t worry folks! It’s not a big problem here. If it gets raises, it would automatically decrease by one point and doesn’t let you give high priority. It shows the result by directing the signal to the low priority in many cases. If you see patterns like below then it’s very normal to react:
1
<1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 173.247.246.116
2
30 ms 7 ms 11 ms 10.10.0.2
3 200 ms 210 ms
189 ms 4.71.136.1
4 111 ms 98 ms
101 ms ip10-167-150-2.at.at.cox.net [70.167.150.2]
5
99 ms 100 ms 98 ms
205.134.225.38
The consistent period when latency in middle acts:
Again, if the hop increases over a certain point in the middle and it remains constant in the same position then it’s not a big deal here. It won’t lead you to get into a problem so, leave it as it is.
1 <1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 173.247.246.116
2
30 ms 7 ms 11 ms 10.10.0.2
3
93 ms 95 ms 92 ms 4.71.136.1
4
95 ms 99 ms 101 ms ip10-167-150-2.at.at.cox.net [70.167.150.2]
5
99 ms 100 ms 98 ms 100ge7-1.core1.nyc4.he.net [184.105.223.166]
6
95 ms 95 ms 95 ms 10g1-3.core1.lax2.he.net [72.52.92.122]
7
95 ms 96 ms 94 ms 205.134.225.38]
Latency increases in the hop at starting: The latency time may increase at the starting point and of course, it leads to problems. Get help from your administrator to deal with this problem!
Timeout at the starting point: If you see hops started in the first or second step don’t worry again it is not a problem here.
Timeout at the last point: There are many reasons for the timeout at the last point. It may show errors on some points.
Without any dependency, we need to analyze the problem right! So, that we can manage and sort out the issue quickly. In this article, we are going to explain how a traceroute can be read even if you are not a technical person. Next time, if your website gives a slow response then you can take a traceroute report and check the status for further confirmation.
What is traceroute mean?
The connection between the website and computer gives a path of points that connects one to one. You can even assume it as a dot-connecting like a chain so that your computer gets the access point of the website immediately. If you are at home or office, the router gives a signal first then goes along with the ISP for connecting the main frequency. There you can see more and more junctions but it won’t go out from the Internet highway and reaches the web server safely.
Here comes the role of traceroute! The path follows from the signal which goes in and around the internet to get connected to the website is known as traceroute. With the guidance of route, the traceroute gives the response time without fail by analyzing the junctions or stops at regular intervals. If you find the time was taken too much in traceroute so, you can confirm there is a problem in your website. In technical terms, they would say as hops instead of stops.
Let us explain how to follow the map of traceroute:
Here, you can see the traceroute report:
As per your request traceroute will start its process and report to you immediately.
In the above report, you can see more rows and columns. As said previously, the route will be traveled with you even if it has a long go. So, the hop is represented as rows, and see the signal step in which direction it moves from one to one. It is known as a check-in point. The rows are categorized into five columns.
This is a sample row with five columns:
10
81 ms 74 ms 74 ms
205.134.225.38
You can consider like
hop is 10 – You can have a count like 10 hops are used here.
RTT1 is 81ms
RTT2 is 74ms
RTT3 is 74ms
IP address: 205.134.225.38
RTT is represented as round trip time. It takes a trip from packet to one essential point and later it reaches the computer. You are well known that ms is nothing but milliseconds. Signal packets are divided into three modes as per traceroute order.
Hop time checks:
Whenever you want to analyze the traceroute, check the round trip time for more pieces of information. Sometimes, you won’t know the existence of the problem due to the increase in time of latency. Give an overall glance at the report and understand the basic requirement first! Up to the United States, if they met trip for 150ms then it’s a long journey but for us, it’s a casual thing. We shouldn’t leave it casually because later it may end up with big issues than we expect.
When latency time increases more than expectation: If the level of the latency reaches more than the target point then please confirm that the issue has been started up in hop. Keep your eye on packets so that, you won’t lose them even if the hop increases at a certain point.
1
10 ms 7 ms 9 ms
172.16.10.2
2
78 ms 100 ms 32 ms
ip10-167-150-2.at.at.cox.net [70.167.150.2]
3
78 ms 84 ms 75 ms
100ge7-1.core1.nyc4.he.net [184.105.223.166]
4
782 ms 799 ms * ms
10gr10-3.core1.lax1.he.net [72.52.92.226]
5
* ms 899 ms 901 ms
10g1-3.core1.lax2.he.net [72.52.92.122]
6
987 ms 954 ms 976 ms
205.134.225.38
7
1002 ms 1011 ms 999 ms
www.hoststud.com [192.145.237.216]
What would happen if latency increases only in the middle point?
Just imagine a situation – Your latency point is normal at starting and ending. But, suddenly it increases in the middle what would be your next step? Don’t worry folks! It’s not a big problem here. If it gets raises, it would automatically decrease by one point and doesn’t let you give high priority. It shows the result by directing the signal to the low priority in many cases. If you see patterns like below then it’s very normal to react:
1
<1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 173.247.246.116
2
30 ms 7 ms 11 ms 10.10.0.2
3 200 ms 210 ms
189 ms 4.71.136.1
4 111 ms 98 ms
101 ms ip10-167-150-2.at.at.cox.net [70.167.150.2]
5
99 ms 100 ms 98 ms
205.134.225.38
The consistent period when latency in middle acts:
Again, if the hop increases over a certain point in the middle and it remains constant in the same position then it’s not a big deal here. It won’t lead you to get into a problem so, leave it as it is.
1 <1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 173.247.246.116
2
30 ms 7 ms 11 ms 10.10.0.2
3
93 ms 95 ms 92 ms 4.71.136.1
4
95 ms 99 ms 101 ms ip10-167-150-2.at.at.cox.net [70.167.150.2]
5
99 ms 100 ms 98 ms 100ge7-1.core1.nyc4.he.net [184.105.223.166]
6
95 ms 95 ms 95 ms 10g1-3.core1.lax2.he.net [72.52.92.122]
7
95 ms 96 ms 94 ms 205.134.225.38]
Latency increases in the hop at starting: The latency time may increase at the starting point and of course, it leads to problems. Get help from your administrator to deal with this problem!
Timeout at the starting point: If you see hops started in the first or second step don’t worry again it is not a problem here.
Timeout at the last point: There are many reasons for the timeout at the last point. It may show errors on some points.
- The firewall in the target will stop the request and it is possible to reach the request using an HTTP request. But have a hope that it won’t result in any connectivity problem.
- The path which is returned may have a problem in the destination. The signal may reach but you may not get a signal to the computer in return cases. Again, you should not get any connection problems.
- Target may have a problem so; your connection will end up in the problem.
